|
IF NOT initDone THEN
initDone:=TRUE;
(*Application specific parameters*)
(*ec_controlUp can be replaced with Joystick's event code if it exists in same control unit*)
S_BoomEndAttenuation.Init(
S_i_PosDirAttenuationLimit := UINT#90,
S_i_NegDirAttenuationLimit := UINT#90,
i_pEventCode := ADR(ec_controlUp),
i_pEventCodePosDirAtt := ADR(S_Inputs.o_EventCode_PosDirAttOn),
i_pEventCodeNegDirAtt := ADR(S_Inputs.o_EventCode_NegDirAttOn)
);
S_BoomControlRamp.Init(
S_i_PosDirAscendRampTime := UINT#1000,
S_i_PosDirDescendRampTime := UINT#1000,
S_i_NegDirAscendRampTime := UINT#1000,
S_i_NegDirDescendRampTime := UINT#1000,
S_i_EnableCounterControl := FALSE,
i_pEventCode := ADR(ec_controlUp)
);
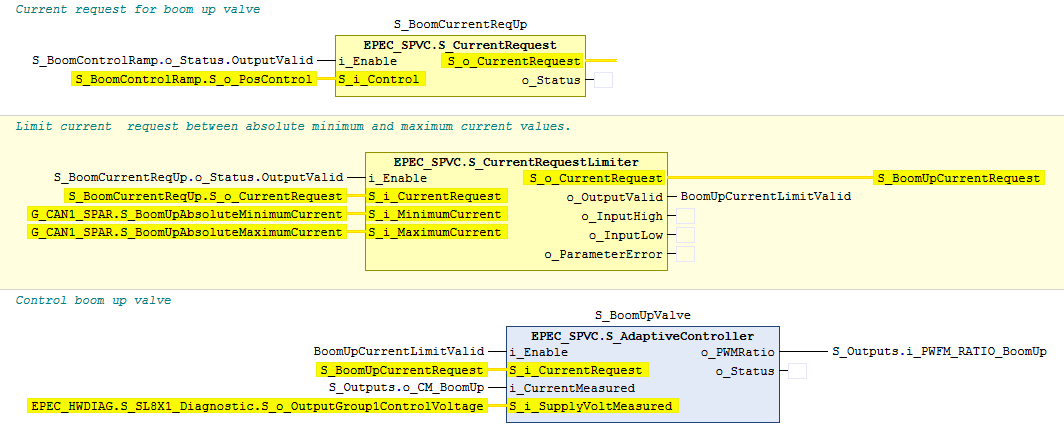
// Note! The minimum and maximum current paremeters can be non-safety parameters
S_BoomCurrentReqUp.Init(
S_i_MinimumCurrent := G_CAN1_PAR.BoomUpMinimumCurrent,
S_i_MaximumCurrent := G_CAN1_PAR.BoomUpMaximumCurrent,
S_i_PositiveControlDir := TRUE,
i_pEventCode := ADR(ec_controlUp)
);
S_BoomUpValve.Init(
S_i_CoilResistance := UDINT#22000,
S_i_OverCurrentLimit := UINT#1100,
S_i_WireBrokenLimit := UINT#50,
S_i_DiagnosticDelay := UINT#100,
i_pCorrectionParameters := ADR(ccParams),
i_pImpulseUpParameters := ADR(ccParamsImpUp),
i_pImpulseDownParameters := ADR(ccParamsImpDown),
S_i_ParameterCount := S_CURRENT_CONTROLLER_PAR_COUNT,
S_i_ParStep := S_CURRENT_CONTROLLER_PAR_STEP,
i_pEventCode := ADR(ec_controlUp)
);
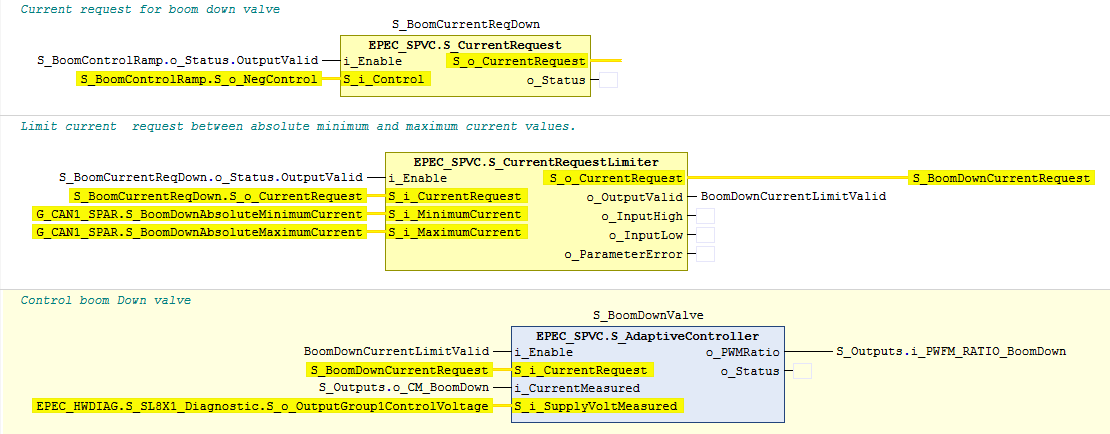
// Note! The minimum and maximum current paremeters can be non-safety parameters
S_BoomCurrentReqDown.Init(
S_i_MinimumCurrent := G_CAN1_PAR.BoomDownMinimumCurrent,
S_i_MaximumCurrent := G_CAN1_PAR.BoomDownMaximumCurrent,
S_i_PositiveControlDir := FALSE,
i_pEventCode := ADR(ec_controlDown)o_
);
S_BoomDownValve.Init(
S_i_CoilResistance := UDINT#22000,
S_i_OverCurrentLimit := UINT#1100,
S_i_WireBrokenLimit := UINT#50,
S_i_DiagnosticDelay := UINT#100,
i_pCorrectionParameters := ADR(ccParams),
i_pImpulseUpParameters := ADR(ccParamsImpUp),
i_pImpulseDownParameters := ADR(ccParamsImpDown),
S_i_ParameterCount := S_CURRENT_CONTROLLER_PAR_COUNT,
S_i_ParStep := S_CURRENT_CONTROLLER_PAR_STEP,
i_pEventCode := ADR(ec_controlDown)
);
END_IF
|
![]()