+5V REF_type080
-
This is an internally regulated and monitored reference voltage supply for external devices.
-
This reference output can be switched on/off by application.
Protection features
-
Overcurrent protection
-
External voltage protection
-
Overheating protection
Voltage monitoring
The level of the output voltage can be monitored by application.
Electrical characteristics
|
Symbol |
Parameter |
Conditions |
Min |
Max |
Units |
|
Vo-level |
Output voltage |
Output On; Unconnected pins |
4,9 |
5,2 |
V |
|
Io |
Nominal Output Current |
Output On; Max total for all pins together |
0 |
500 |
mA |
|
Io-lim |
Internal Current Limitation |
Output On (Note 2, 3) |
typ. 2 |
A |
|
|
Co |
Output Capacitance |
|
typ. 60,8 |
uF |
|
|
VI-max |
Max Input voltage |
Overload conditions (Note 1) |
|
36 |
V |
|
Voltage monitoring |
|||||
|
VI-range |
Nominal Voltage measuring range |
|
0 |
5,9 |
V |
Note 1: When output voltage is under overload conditions, for example, short circuit to supply voltages. Exceeding the max value might cause damage to output.
Note 2: Current limit for overcurrent protection to limit internal power dissipation.
Note 3: When the limit is exceeded, the output current is regulated. For more information refer to Epec Programming and Libraries Manual.
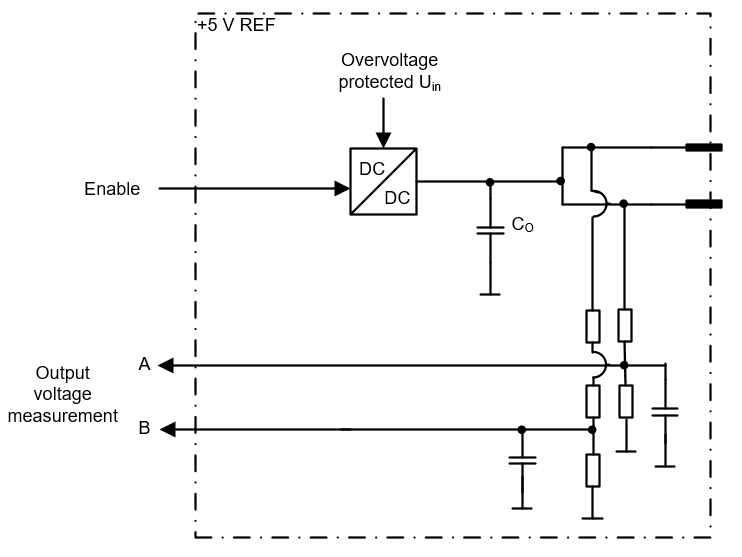
Functional block diagram
Under / Overvoltage Diagnostics
-
Under / overvoltage can be detected using the output voltage monitoring feature, that can be implemented by using function block S_RefControlAndDiagnostics from the library SafeSSeriesHardware.
-
If the output voltage monitoring value is over 5,2 V, it is determined in the application that an external voltage source is connected to the output.
|
|
In case of a limit violation, the output should be disabled as soon as possible. The control unit can handle short term errors, but long term (e.g. several hours) exposures should be avoided with application/system design. Long term exposure to overvoltage or overload can cause permanent damage to the unit.
|